前言 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 <servlet > <servlet-name > spring-mvc</servlet-name > <servlet-class > org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class > <init-param > <param-name > contextConfigLocation</param-name > <param-value > classpath:config/spring-mvc.xml</param-value > </init-param > <load-on-startup > 1</load-on-startup > </servlet > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > spring-mvc</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping >
根据web.xml的配置,我们可以知道springMVC的主体控制器部分就是DispatcherServlet,同时也不难看出DispatcherServlet的本质其实就是一个Servlet。那我们这次来剖析一下DispatcherServlet的初始化流程。
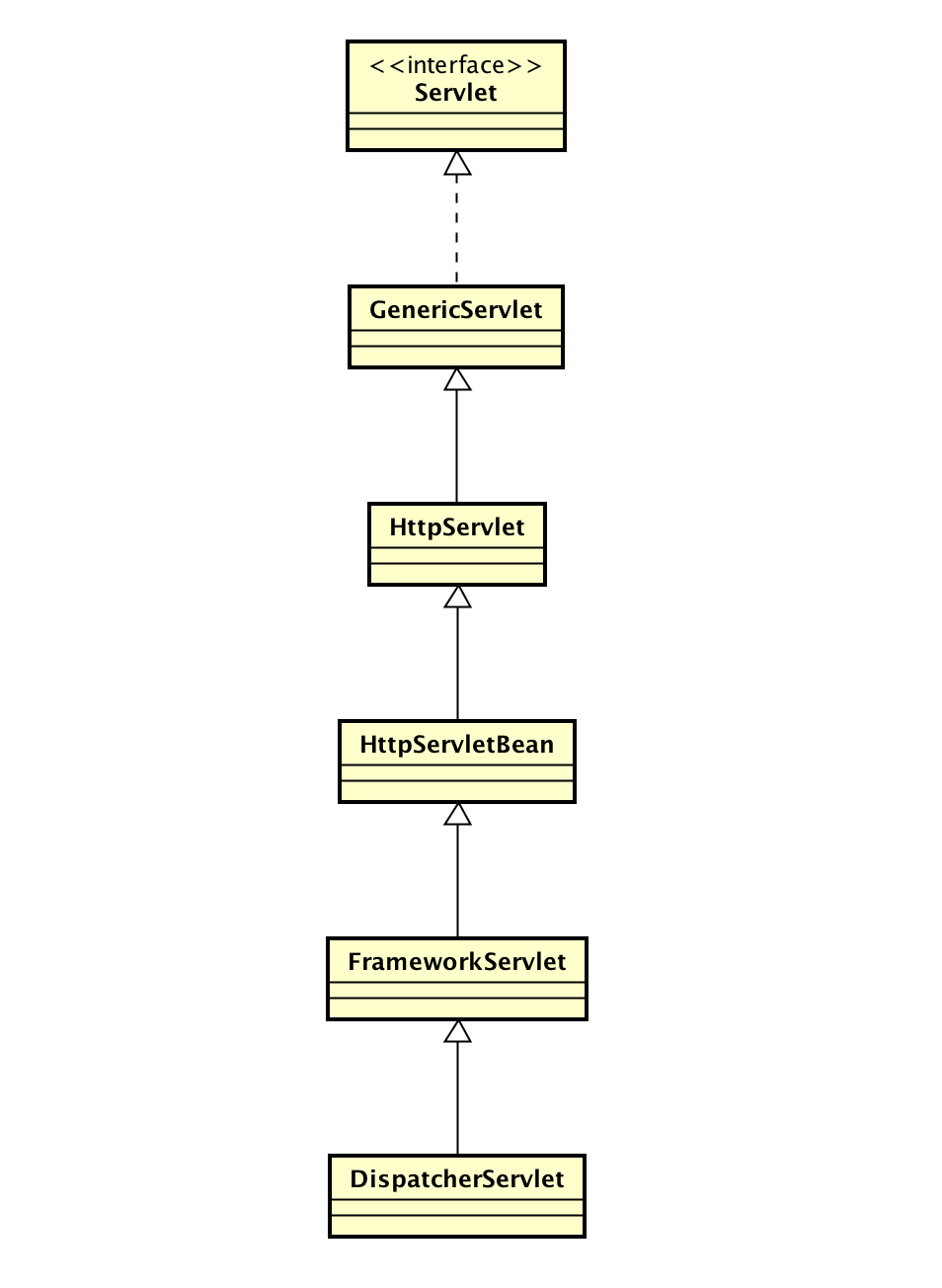
DispatcherServlet类图
其中HttpServletBean、FrameworkServlet和DispatcherServlet都是springMVC框架中的东西。
HttpServletBean类的init方法 写java web时,我们知道如果需要初始化,那我们就需要重载HttpServlet的init方法。那么我们首先来寻找init方法的位置,可以发现它在HttpServletBean类中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 public final void init () throws ServletException if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + getServletName() + "'" ); } try { PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this .requiredProperties); BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this ); ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext()); bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment())); initBeanWrapper(bw); bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true ); } catch (BeansException ex) { logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'" , ex); throw ex; } initServletBean(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully" ); } }
该方法主要做了如下两件事:
将初始化参数设置为该servlet的属性
调用子类的initServletBean方法
附:以我的理解来解释一下初始化参数设置为属性这一步骤,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 <servlet > <servlet-name > spring-mvc</servlet-name > <servlet-class > org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class > <init-param > <param-name > contextConfigLocation</param-name > <param-value > classpath:config/spring-mvc.xml</param-value > </init-param > <load-on-startup > 1</load-on-startup > </servlet > <servlet-mapping > <servlet-name > spring-mvc</servlet-name > <url-pattern > /</url-pattern > </servlet-mapping >
在配置文件中我们可以发现DispatcherServlet的初始化参数为contextConfigLocation=classpath:config/spring-mvc.xml,我们可以在FrameworkServlet的属性列表中找到contextConfigLocation这个属性。那么这块地方做的工作就是将初始化参数中contextConfigLocation的值配置给DispatcherServlet的contextConfigLocation属性。
FrameworkServlet类的initServletBean方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 protected final void initServletBean () throws ServletException getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'" ); if (this .logger.isInfoEnabled()) { this .logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started" ); } long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { this .webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext(); initFrameworkServlet(); } catch (ServletException ex) { this .logger.error("Context initialization failed" , ex); throw ex; } catch (RuntimeException ex) { this .logger.error("Context initialization failed" , ex); throw ex; } if (this .logger.isInfoEnabled()) { long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime; this .logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms" ); } }
该函数中主要调用了两个方法:initWebApplicationContext()和initFrameworkServlet()。
initFrameworkServlet()是用来给子类做初始化扩展的,事实上FrameworkServlet中是一个空实现,DispatchServlet也并没有重载该方法。
FrameworkServlet类的initWebApplicationContext方法 初始化WebApplicationContext,并且将根WebApplicationContext设置为其父context。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext () WebApplicationContext rootContext = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext()); WebApplicationContext wac = null ; if (this .webApplicationContext != null ) { wac = this .webApplicationContext; if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac; if (!cwac.isActive()) { if (cwac.getParent() == null ) { cwac.setParent(rootContext); } configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac); } } } if (wac == null ) { wac = findWebApplicationContext(); } if (wac == null ) { wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext); } if (!this .refreshEventReceived) { onRefresh(wac); } if (this .publishContext) { String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName(); getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac); if (this .logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this .logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() + "' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]" ); } } return wac; }
DispatcherServlet类的onRefresh方法 我们可以发现,无论怎样,initWebApplicationContext方法最终都会调用到onRefresh方法。onRefresh在DispatcherServlet中被重载了,那我们直接看onRefresh部分的源码。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 protected void onRefresh (ApplicationContext context) initStrategies(context); } protected void initStrategies (ApplicationContext context) initMultipartResolver(context); initLocaleResolver(context); initThemeResolver(context); initHandlerMappings(context); initHandlerAdapters(context); initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); initViewResolvers(context); initFlashMapManager(context); }
我们可以看到onRefresh调用了initStrategies方法,而initStrategies则对MultipartResolver, LocaleResolver, ThemeResolve, HandlerMappings, HandlerAdapters, HandlerExceptionResolvers, RequestToViewNameTranslator, ViewResolvers和FlashMapManager做了初始化。
不难知道,我们之前阅读的HandlerMapping, HandlerAdapter及ViewResolver等都是在这一步进行初始化的操作。
initHandlerMappings 我们取其中的HandlerMapping的初始化来继续分析初始化流程,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 private void initHandlerMappings (ApplicationContext context) this .handlerMappings = null ; if (this .detectAllHandlerMappings) { Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true , false ); if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) { this .handlerMappings = new ArrayList<HandlerMapping>(matchingBeans.values()); OrderComparator.sort(this .handlerMappings); } } else { try { HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class); this .handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm); } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { } } if (this .handlerMappings == null ) { this .handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("No HandlerMappings found in servlet '" + getServletName() + "': using default" ); } } }
从源码中可以知道,HandlerMapping的初始化流程主要分为两种,
使用用户自己的配置
使用默认配置
对于自己的配置没有什么可说的,那我们接下来来看默认配置,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 protected <T> List<T> getDefaultStrategies (ApplicationContext context, Class<T> strategyInterface) { String key = strategyInterface.getName(); String value = defaultStrategies.getProperty(key); if (value != null ) { String[] classNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(value); List<T> strategies = new ArrayList<T>(classNames.length); for (String className : classNames) { try { Class<?> clazz = ClassUtils.forName(className, DispatcherServlet.class.getClassLoader()); Object strategy = createDefaultStrategy(context, clazz); strategies.add((T) strategy); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { throw new BeanInitializationException( "Could not find DispatcherServlet's default strategy class [" + className + "] for interface [" + key + "]" , ex); } catch (LinkageError err) { throw new BeanInitializationException( "Error loading DispatcherServlet's default strategy class [" + className + "] for interface [" + key + "]: problem with class file or dependent class" , err); } } return strategies; } else { return new LinkedList<T>(); } }
我们可以看到里面有一个关键的属性defaultStrategies。我们来看看这个defaultStrategies到底是怎么一回事,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = "DispatcherServlet.properties" ;private static final Properties defaultStrategies;static { try { ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, DispatcherServlet.class); defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); } catch (IOException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'DispatcherServlet.properties': " + ex.getMessage()); } }
可以发现defaultStrategies里的属性来自于DispatcherServlet.properties这个文件,那么我们继续找到该文件,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver =org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.ThemeResolver =org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping =org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\ org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter =org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\ org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\ org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver =org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerExceptionResolver,\ org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver,\ org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator =org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver =org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMapManager =org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager
到这里我们的疑惑应该就已经全部解清了。也知道之前阅读的HandlerMapping、HandlerAdater等默认值为什么是那些了。当然了,如果我们只需要其中的部分HandlerMapping等,也并不需要修改该文件,从getDefaultStrategies函数中我们可以知道,只需要我们在配置文件中有定义相应的属性,那么就不会使用默认的。